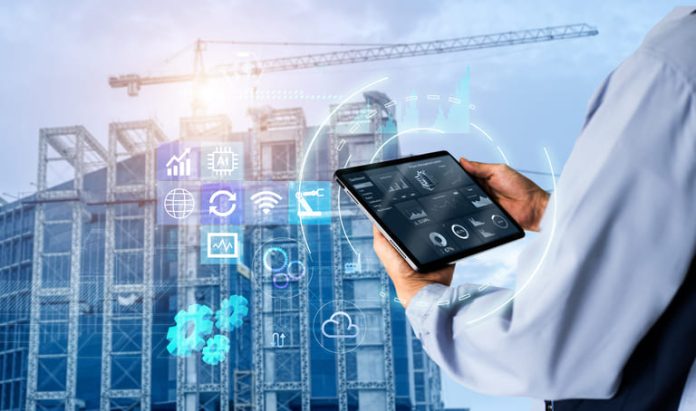
The future of real estate is being reshaped by the integration of cutting-edge technology into building management. Smart buildings, which leverage the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and automation, are revolutionizing the industry by enhancing energy efficiency, tenant comfort, and operational cost savings. These advancements are crucial as the built environment accounts for 39% of global carbon emissions, necessitating smarter, more sustainable solutions.
Revolutionizing Building Management
Smart buildings represent a paradigm shift in how real estate is managed, focusing on optimizing energy use and occupant comfort through sophisticated technology. By processing real-time data, these buildings can monitor, control, and adjust various systems to maintain optimal performance and efficiency. Read more at https://resustain.com/
The use of IoT sensors, AI systems, and automated controls enables smart buildings to operate more sustainably. For example, IoT sensors can track occupancy, temperature, and air quality, providing data that AI systems analyze to predict energy usage patterns. Automated controls then adjust lighting, heating, and cooling systems accordingly, reducing energy consumption and costs.
Key Components of Smart Buildings
- IoT Sensors: These devices collect real-time data on various aspects of the building environment, such as occupancy levels, temperature, humidity, and air quality. This data is essential for making informed decisions about energy use and building operations.
- AI Systems: AI algorithms analyze the data collected by IoT sensors to identify patterns and predict future energy needs. By learning from past data, AI systems can optimize building performance, ensuring that energy is used efficiently and only when necessary.
- Automated Controls: These systems use the insights provided by AI to automatically adjust building operations. For instance, lighting and HVAC systems can be controlled to reduce energy use during non-peak hours or when spaces are unoccupied.
- Data Analytics: Comprehensive data analytics provide insights into building performance, helping facility managers identify areas for improvement and track progress towards sustainability goals. This continuous feedback loop ensures that buildings remain energy-efficient and environmentally friendly.
Benefits of Smart Buildings
Smart buildings offer numerous benefits beyond energy efficiency and sustainability. These include improved tenant comfort, enhanced security, and increased property value. By creating a more comfortable and secure environment, smart buildings can attract and retain tenants, boosting occupancy rates and rental income.
- Energy Savings: Smart buildings can significantly reduce energy consumption through optimized operations. This not only lowers utility costs but also reduces the carbon footprint of the building, contributing to global sustainability efforts.
- Tenant Comfort: By maintaining optimal indoor conditions, smart buildings enhance tenant comfort and well-being. This can lead to increased tenant satisfaction and retention, as well as improved productivity in commercial settings.
- Enhanced Security: Smart buildings often incorporate advanced security systems that use AI and IoT to monitor and respond to security threats in real-time. This provides a safer environment for tenants and reduces the risk of security breaches.
- Increased Property Value: Buildings that are energy-efficient and technologically advanced tend to have higher market values. Investors and buyers are increasingly looking for properties that offer sustainability and smart features, making smart buildings more attractive investments.
Implementing Smart Building Technologies
Transitioning to smart buildings requires careful planning and execution. Here are the key steps to successfully implement smart building technologies:
- Assessment and Planning: Conduct a thorough assessment of the building’s current systems and identify areas where smart technologies can be integrated. Develop a comprehensive plan that outlines the goals, timeline, and budget for the transition.
- Infrastructure Upgrades: Upgrade the building’s infrastructure to support smart technologies. This may include installing IoT sensors, upgrading HVAC and lighting systems, and enhancing network connectivity.
- System Integration: Integrate the various smart technologies into a cohesive system. This involves connecting IoT sensors, AI systems, and automated controls to a central building management system (BMS) that can monitor and control operations.
- Training and Support: Provide training and support to facility managers and staff to ensure they understand how to use the new systems effectively. Ongoing support and maintenance are also crucial to keep the systems running smoothly.
- Continuous Improvement: Monitor the performance of the smart building systems and make adjustments as needed. Use data analytics to identify areas for improvement and optimize operations over time.
The Path Forward
Smart buildings represent the future of real estate management, offering a sustainable and efficient solution to the challenges facing the industry. By leveraging advanced technology, smart buildings can significantly reduce energy consumption and carbon emissions, while enhancing tenant comfort and property value.
As the real estate sector continues to evolve, the adoption of smart building technologies will become increasingly important. Embracing these innovations will not only help meet sustainability goals but also create more resilient and adaptable buildings that can thrive in the changing landscape of real estate.