By Mostafa Sayyadi and Michael Provitera
The world of business is exposed to rapid changes, and corporate social innovation has become a key way for companies to resolve social problems while growing their businesses. This article shows how effective leadership in corporate social innovation, which we call as Conscious Leadership Model, can make a big difference in the business world.
Introduction
We cover the six critical ingredients for strong corporate social innovation initiatives to successfully leverage a company’s capacities and assets for the greater social good. Leadership vision and commitment is one of these six critical ingredients. Next, this article points out the Conscious Leadership Model that can make corporate social innovation leadership successful, helping businesses use their resources and skills to make a social impact. We thoroughly examine this new leadership model to cultivate effective corporate leadership for social innovation. The article also continues talking about how to include corporate social innovation in a company’s conscious leadership. The narrative shows how innovation can be linked to corporate leadership, providing a detailed model of how to incorporate corporate social innovation into conscious leadership. In particular, we provide the three-step learning process to effectively integrate corporate social innovation into corporate leadership – meeting business objectives while considering social issues. Our mission is to offer guidance on advancing corporate social innovation, like launching small pilot projects and aligning business objectives with social impact.
Companies that are breaking the mold are moving beyond corporate social responsibility to social innovation. These companies are the vanguard of the new paradigm. They view community needs as opportunities to develop ideas and demonstrate business technologies, to find and serve new markets, and to solve longstanding business problems. ____ Rosabeth Moss Kanter [1]
The Six Ingredients of Strong Corporate Social Innovation Initiatives
First, let’s look at this handy guide for leaders seeking to embrace corporate social innovation as an innovation and growth strategy in their corporate leadership. Corporate social innovation involves companies finding creative solutions to social problems using their available resources and talent. [2] [3] [4] The following critical ingredients should underpin any comprehensive definition of corporate social innovation. These include:
1. Leadership Vision and Commitment
The first ingredient of strong corporate social innovation initiatives is leadership vision and commitment in which leaders play a pivotal role in setting their company’s social vision, embedding social value creation within company cultures, and nurturing an atmosphere supportive of this activity. Leaders’ support and dedication play a crucial role in mobilizing stakeholders, allocating resources, and driving social innovation initiatives forward. [5] [6] [7]
2. Shared Value Creation
Second, we also use what we call shared value creation, and we build upon this idea through corporate social innovation actions and beyond their benefits for society, creating tangible and intangible economic value for businesses through tangible and intangible measures of social return on investment (ROI).
3. An Effective Structure and Culture to Drive Social Value Creation
The third ingredient of strong corporate social innovation initiatives is an effective structure and culture to drive social value creation. Here we integrate social innovation into an organization which involves taking into account its business model, its structure, its system, and most importantly, its culture. In particular, responsiveness to society must be prioritized to foster lasting social value creation. [8] [9] [10]
4. Stakeholder Involvement
The next ingredient of strong corporate social innovation initiatives is stakeholder involvement. [11] [12] [13] External stakeholders such as civil society, public institutions, and non-government organizations (NGOs) play an essential role in defining social problems and finding suitable solutions. In addition, executives should not take away from the employees, who constitute the first stakeholder group in the city.
5. Social Empathy and Awareness
The fifth ingredient of strong corporate social innovation initiatives is social empathy and awareness. [14] [15] For an enterprise to successfully undertake social innovation initiatives, its social empathy and awareness capabilities must be strong and continually developed concerning particular social challenges it must confront and then look for bold, innovative solutions to overcome them. Incorporating this dimension underlines the necessity of industry-specific social innovation initiatives.
6. Ability to Innovate when Solving Social Problems
The last ingredient of strong corporate social innovation initiatives is the ability to innovate when solving social problems. Many of the organizations have capitalized on the significance of corporate social innovation capabilities. These corporations have demonstrated they are adept at finding novel approaches for solving societal challenges using skills and technology while creating methodologies that benefit society and business.
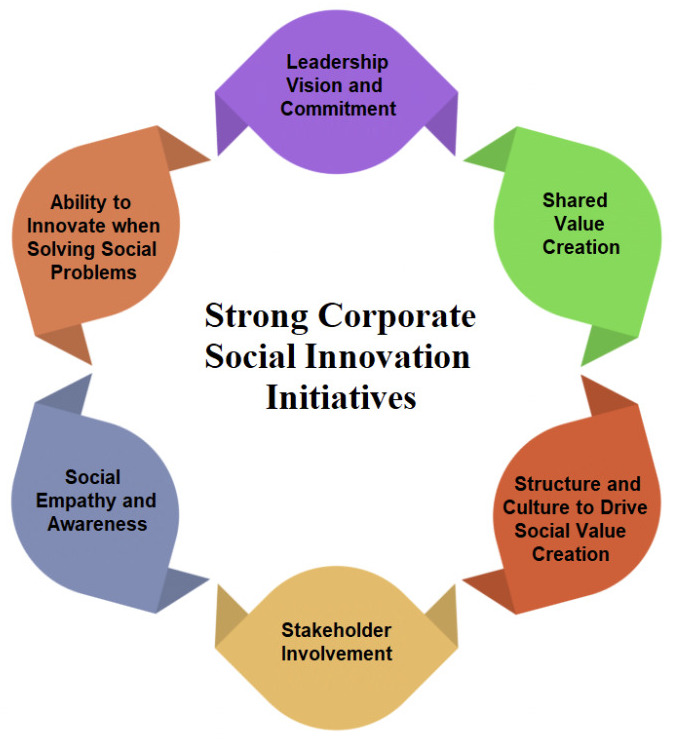
Figure 1: The Six Ingredients of Strong Corporate Social Innovation Initiatives
Conscious Leadership Model
Executives can develop conscious leadership through implement the following three-step learning process:
- Step One: run a Got Want Gap Analysis
- Step Two: record the want portion of the analysis coupled with the strategy situation initiatives.
- Step Three: implement three intangible strategic initiatives. One incorporating Human capital, two, incorporating Organizational Capital, and three, expanding the organizational social capital.
We suggest that leaders start by launching small pilot projects for social innovation. When those are successful, the lessons learned can be used to expand the efforts more broadly. Training all employees at all company levels on social issues is also crucial. This builds an understanding so everyone can help come up with solutions.
Defining and tracking clear metrics also lets you monitor the social and business value created. [16] Check on progress regularly to stay accountable. Developing processes to gather input from different groups, including their needs and perspectives, keeps solutions focused on what matters most to society. Visibly rewarding and praising employees for demonstrating the desired values and behaviors is a positive reinforcement.
When corporate social innovation is approached carefully, with dedicated effort over time, leaders can transform culture to embed social responsibility fully. This ultimately leads to positive change for communities and builds long-term value for the company.
The Main Challenges Ahead
Executives can develop conscious leadership to create innovative solutions to social problems. However, employees don’t want to change up their regular routines to do new socially focused stuff. Plus, it’s hard to measure whether the social projects are making a difference for people. So, it’s very tough to know the real value created. Furthermore, executives face many other challenges – getting people on board, balancing business and social goals, showing the impact, and dealing with more opinions. It’s tough. But if they stay committed and keep working at it, companies can push through the obstacles in progress.
In Conclusion
This article delves into understanding how effective leadership in corporate social innovation can provide more innovative solutions to solve social problems and bring about positive social change. This article aims to understand how the leadership of corporate social innovation can effectively address social challenges and contribute to sustainable and inclusive development. This article highlights the growing importance of integrating corporate leadership in social innovation research. To do this, this article proposes the Conscious Leadership Model to foster sustainable practices and approaches within corporate social innovation initiatives. The prominence of these discussions is reflected in this proposed three-step learning process related to corporate social innovation in the field.
About the Authors
 Mostafa Sayyadi works with senior business leaders to effectively develop innovation in companies, and helps companies—from start-ups to the Fortune 100—succeed by improving the effectiveness of their leaders.
Mostafa Sayyadi works with senior business leaders to effectively develop innovation in companies, and helps companies—from start-ups to the Fortune 100—succeed by improving the effectiveness of their leaders.
 Michael J. Provitera is an Associate Professor at Barry University. He is an author of Level Up Leadership published by Business Expert Press.
Michael J. Provitera is an Associate Professor at Barry University. He is an author of Level Up Leadership published by Business Expert Press.
References
- [1] Kanter, R.M. (1999). From Spare Change to Real Change: The Social Sector as Beta Site for Business Innovation. Harvard Business Review (May-June, 1999). https://hbr.org/1999/05/from-spare-change-to-real-change-the-social-sector-as-beta-site-for-business-innovation
- [2] Riano, .D., Yakovleva, N. (2019). Corporate Social Responsibility. In: Leal Filho, W., Azul, A., Brandli, L., Özuyar, P., Wall, T. (eds) Responsible Consumption and Production. Encyclopedia of the UN Sustainable Development Goals. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-71062-4_26-1
- [3] Jiang, L. (2021). Definitions of Corporate Social Responsibility. In: Crowther, D., Seifi, S. (eds) The Palgrave Handbook of Corporate Social Responsibility. Palgrave Macmillan, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-42465-7_1
- [4] Chu, M., Muhamad, H.B., Mustapha, M.B., San, O.T., Zan, F. & Jia, X. (2022). Research Trends in Corporate Social Responsibility and Innovation: A Bibliometric Analysis. Sustainability, 14(21), p. 14185. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142114185
- [5] Porter, M. E. & Kramer, M. R. (2006). Strategy & society: The link between competitive advantage and corporate social responsibility. Harvard Business Review, 84(12), pp. 78-92. https://hbr.org/2006/12/strategy-and-society-the-link-between-competitive-advantage-and-corporate-social-responsibility
- [6] Wirba, A.V. (2023). Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): The Role of Government in promoting CSR. Journal of the Knowledge Economy. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13132-023-01185-0
- [7] Pless, N.M., Sengupta, A., Wheeler, M.A. & Makk, T. (2022). Responsible Leadership and the Reflective CEO: Resolving Stakeholder Conflict by Imagining What Could Be Done. Journal of Business Ethics 180(1), 313–337. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-021-04865-6
- [8] Bertello, A., De Bernardi, P. & Ricciardi, F. (2023). Open innovation: status quo and quo vadis – an analysis of a research field. Review of Managerial Science. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11846-023-00655-8
- [9] Braunerhjelm, P. & Henrekson, M. (2024). Policies to Stimulate Innovation and Entrepreneurship. In: Unleashing Society’s Innovative Capacity. International Studies in Entrepreneurship, vol 55. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-42756-5_4
- [10] Chalmers, D. (2013). Social innovation: An exploration of the barriers faced by innovating organizations in the social economy. Local Economy, 28 (1), 17–34. https://doi.org/10.1177/02690942124636
- [11] Zu, L. (2013). Social Innovation. In: Idowu, S.O., Capaldi, N., Zu, L., Gupta, A.D. (eds) Encyclopedia of Corporate Social Responsibility. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-28036-8_252
- [12] Eschweiler, J. & Dupret, K. (2023). Introduction. In: Langergaard, L.L., Dupret, K., Eschweiler, J. (eds) Learning about Social Entrepreneurship and Management in Times of Social Transformation. Ethical Economy, vol 66. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-47708-9_1
- [13] Tapaninaho, R. & Kujala, J. (2019). Reviewing the Stakeholder Value Creation Literature: Towards a Sustainability Approach. In: Leal Filho, W. (eds) Social Responsibility and Sustainability. World Sustainability Series. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-03562-4_1
- [14] Lashitew, A.A., Narayan, S., Rosca, E. & Bals, L. (2022). Creating Social Value for the ‘Base of the Pyramid’: An Integrative Review and Research Agenda. Journal of Business Ethics 178(2), 445–466. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-020-04710-2
- [15] Osburg, T. (2013). Social Innovation to Drive Corporate Sustainability, CSR, Sustainability, Ethics & Governance, In: Thomas Osburg & René Schmidpeter (Eds.), Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-36540-9_2
- [16] Fabbe-Costes, N. (2023). Performance Measurement – Value Creation. In: Sarkis, J. (eds) The Palgrave Handbook of Supply Chain Management. Palgrave Macmillan, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-89822-9_28-1